
国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 323-328.doi: 10.12280/gjszjk.20230024
收稿日期:2023-01-18
出版日期:2023-07-15
发布日期:2023-07-26
通讯作者:
汪丽萍
E-mail:wlilyu@hotmail.com
基金资助:
GUO Yan, DIAO Rui-ying, SU Dan-na, WANG Li-ping( )
)
Received:2023-01-18
Published:2023-07-15
Online:2023-07-26
Contact:
WANG Li-ping
E-mail:wlilyu@hotmail.com
摘要:
卵巢内存在复杂的神经-内分泌和免疫调控网络。组织驻留巨噬细胞(tissue-resident macrophages,TRM)是一类存在于人体绝大多数组织器官、独立于外周循环且具有一定自我更新能力的固有免疫细胞,卵巢TRM是卵巢中最丰富的免疫细胞,主要驻留在卵泡膜、黄体、闭锁卵泡和间质组织等构成的微环境中;其数目、分布、功能稳态异常可影响卵泡发育(包括卵母细胞成熟和排卵等),与女性不孕相关。卵巢TRM功能障碍会导致卵巢常见疾病发生,如卵巢子宫内膜异位囊肿、多囊卵巢综合征和早发性卵巢功能不全等。综述卵巢TRM的来源、生理功能及其功能异常对卵泡发育的影响机制,并对卵巢TRM功能障碍相关卵巢疾病进行深入探讨,旨在为卵巢功能障碍性疾病的治疗提供新的思路。
郭艳, 刁瑞英, 苏丹娜, 汪丽萍. 组织驻留巨噬细胞与卵巢常见疾病[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2023, 42(4): 323-328.
GUO Yan, DIAO Rui-ying, SU Dan-na, WANG Li-ping. Tissue-Resident Macrophages and Common Ovarian Diseases[J]. Journal of International Reproductive Health/Family Planning, 2023, 42(4): 323-328.
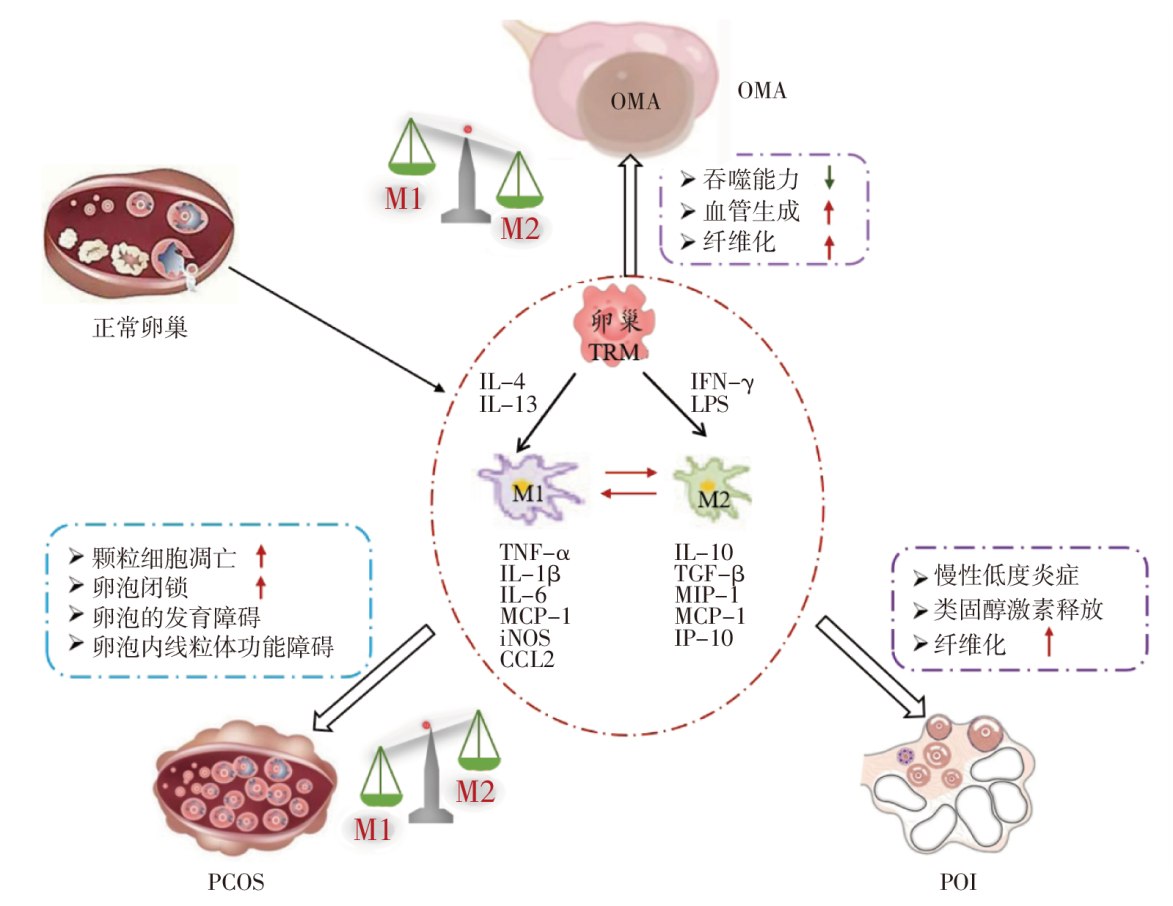
图1 卵巢TRM的表型转化与卵巢功能障碍相关疾病的相关性 注:OMA 卵巢子宫内膜异位囊肿,PCOS 多囊卵巢综合征,POI 早发性卵巢功能不全,M1 M1型巨噬细胞,IL-4 白细胞介素-4,TNF-α 肿瘤坏死因子α,MCP-1 单核细胞趋化蛋白-1,iNOS 诱导型一氧化氮合酶,CCL2 CC趋化因子配体2。
| [1] |
Wu R, Van der Hoek KH, Ryan NK, et al. Macrophage contributions to ovarian function[J]. Hum Reprod Update, 2004, 10(2):119-133. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmh011.
doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmh011 pmid: 15073142 |
| [2] |
Zhang Z, Schlamp F, Huang L, et al. Inflammaging is associated with shifted macrophage ontogeny and polarization in the aging mouse ovary[J]. Reproduction, 2020, 159(3):325-337. doi: 10.1530/REP-19-0330.
doi: 10.1530/REP-19-0330 pmid: 31940276 |
| [3] |
Turner EC, Hughes J, Wilson H, et al. Conditional ablation of macrophages disrupts ovarian vasculature[J]. Reproduction, 2011, 141(6):821-831. doi: 10.1530/REP-10-0327.
doi: 10.1530/REP-10-0327 pmid: 21393340 |
| [4] |
Jokela H, Lokka E, Kiviranta M, et al. Fetal-derived macrophages persist and sequentially maturate in ovaries after birth in mice[J]. Eur J Immunol, 2020, 50(10):1500-1514. doi: 10.1002/eji.202048531.
doi: 10.1002/eji.202048531 URL |
| [5] |
Li N, Li Z, Fang F, et al. Two distinct resident macrophage populations coexist in the ovary[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13:1007711. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1007711.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1007711 URL |
| [6] |
李念娱, 焦雪, 秦莹莹. 性腺组织驻留巨噬细胞的研究进展[J]. 中华生殖与避孕杂志, 2022, 42(4):419-424. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn101441-20200901-00472.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn101441-20200901-00472 |
| [7] |
Sun JX, Xu XH, Jin L. Effects of Metabolism on Macrophage Polarization Under Different Disease Backgrounds[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13:880286. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.880286.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.880286 URL |
| [8] |
Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S, Vazini H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(9):6425-6440. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26429.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.26429 pmid: 29319160 |
| [9] |
Duffy DM, Ko C, Jo M, et al. Ovulation: Parallels With Inflammatory Processes[J]. Endocr Rev, 2019, 40(2):369-416. doi: 10.1210/er.2018-00075.
doi: 10.1210/er.2018-00075 pmid: 30496379 |
| [10] |
Caillaud M, Duchamp G, Gérard N. In vivo effect of interleukin-1beta and interleukin-1RA on oocyte cytoplasmic maturation, ovulation, and early embryonic development in the mare[J]. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 2005, 3:26. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-3-26.
doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-3-26 |
| [11] |
Zhu Y. Metalloproteases in gonad formation and ovulation[J]. Gen Comp Endocrinol, 2021, 314:113924. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2021.113924.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2021.113924 URL |
| [12] |
赵久华, 郑舒婷, 林凤屏, 等. 免疫细胞在黄体发育及退化过程中的作用[J]. 中国医学科学院学报, 2022, 44(3):504-509. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.13309.
doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.13309 |
| [13] |
Wu J, Carlock C, Zhou C, et al. IL-33 is required for disposal of unnecessary cells during ovarian atresia through regulation of autophagy and macrophage migration[J]. J Immunol, 2015, 194(5):2140-2147. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402503.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402503 pmid: 25617473 |
| [14] |
Cui LL, Yang G, Pan J, et al. Tumor necrosis factor α knockout increases fertility of mice[J]. Theriogenology, 2011, 75(5):867-876. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2010.10.029.
doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2010.10.029 URL |
| [15] |
Pepe G, Locati M, Della Torre S, et al. The estrogen-macrophage interplay in the homeostasis of the female reproductive tract[J]. Hum Reprod Update, 2018, 24(6):652-672. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmy026.
doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmy026 pmid: 30256960 |
| [16] |
Liang Y, Xie H, Wu J, et al. Villainous role of estrogen in macrophage-nerve interaction in endometriosis[J]. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 2018, 16(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12958-018-0441-z.
doi: 10.1186/s12958-018-0441-z |
| [17] |
Ono Y, Nagai M, Yoshino O, et al. CD11c+ M1-like macrophages (MΦs) but not CD206+ M2-like MΦ are involved in folliculogenesis in mice ovary[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1):8171. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25837-3.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25837-3 pmid: 29802255 |
| [18] |
McFee RM, Rozell TG, Cupp AS. The balance of proangiogenic and antiangiogenic VEGFA isoforms regulate follicle development[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2012, 349(3):635-647. doi: 10.1007/s00441-012-1330-y.
doi: 10.1007/s00441-012-1330-y pmid: 22322423 |
| [19] |
Rizov M, Andreeva P, Dimova I. Molecular regulation and role of angiogenesis in reproduction[J]. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol, 2017, 56(2):127-132. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2016.06.019.
doi: S1028-4559(17)30001-3 pmid: 28420494 |
| [20] |
Zeng XY, Xie H, Yuan J, et al. M2-like tumor-associated macrophages-secreted EGF promotes epithelial ovarian cancer metastasis via activating EGFR-ERK signaling and suppressing lncRNA LIMT expression[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2019, 20(7):956-966. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1564567.
doi: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1564567 URL |
| [21] |
Tan Z, Gong X, Li Y, et al. Impacts of endometrioma on ovarian aging from basic science to clinical management[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2022, 13:1073261. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1073261.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1073261 |
| [22] |
Taylor HS, Kotlyar AM, Flores VA. Endometriosis is a chronic systemic disease: clinical challenges and novel innovations[J]. Lancet, 2021, 397(10276):839-852. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00389-5.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00389-5 pmid: 33640070 |
| [23] |
Laganà AS, Salmeri FM, Ban Frangež H, et al. Evaluation of M1 and M2 macrophages in ovarian endometriomas from women affected by endometriosis at different stages of the disease[J]. Gynecol Endocrinol, 2020, 36(5):441-444. doi: 10.1080/09513590.2019.1683821.
doi: 10.1080/09513590.2019.1683821 pmid: 31663401 |
| [24] |
Liu X, Zhang Q, Guo SW. Histological and Immunohistochemical Characterization of the Similarity and Difference Between Ovarian Endometriomas and Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis[J]. Reprod Sci, 2018, 25(3):329-340. doi: 10.1177/1933719117718275.
doi: 10.1177/1933719117718275 pmid: 28718381 |
| [25] |
Filippi I, Carrarelli P, Luisi S, et al. Different Expression of Hypoxic and Angiogenic Factors in Human Endometriotic Lesions[J]. Reprod Sci, 2016, 23(4):492-497. doi: 10.1177/1933719115607978.
doi: 10.1177/1933719115607978 pmid: 26408396 |
| [26] |
Zhang D, Yu Y, Duan T, et al. The role of macrophages in reproductive-related diseases[J]. Heliyon, 2022, 8(11):e11686. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11686.
doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11686 URL |
| [27] |
Xiong YL, Liang XY, Yang X, et al. Low-grade chronic inflammation in the peripheral blood and ovaries of women with polycystic ovarian syndrome[J]. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol, 2011, 159(1):148-150. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2011.07.012.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2011.07.012 URL |
| [28] |
Goteri G, Lucarini G, Zizzi A, et al. Proangiogenetic molecules, hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and nitric oxide synthase isoforms in ovarian endometriotic cysts[J]. Virchows Arch, 2010, 456(6):703-710. doi: 10.1007/s00428-010-0929-1.
doi: 10.1007/s00428-010-0929-1 URL |
| [29] |
Chon SJ, Umair Z, Yoon MS. Premature Ovarian Insufficiency: Past, Present, and Future[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9:672890. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.672890.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.672890 URL |
| [30] |
Ishizuka B. Current Understanding of the Etiology, Symptomatology, and Treatment Options in Premature Ovarian Insufficiency (POI)[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2021, 12:626924. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.626924.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.626924 |
| [31] |
Liu P, Zhang X, Hu J, et al. Dysregulated cytokine profile associated with biochemical premature ovarian insufficiency[J]. Am J Reprod Immunol, 2020, 84(4):e13292. doi: 10.1111/aji.13292.
doi: 10.1111/aji.13292 |
| [32] |
Taghavi SA, Ashrafi M, Mehdizadeh M, et al. Toll-like receptors expression in follicular cells of patients with poor ovarian response[J]. Int J Fertil Steril, 2014, 8(2):183-192.
pmid: 25083184 |
| [33] |
Briley SM, Jasti S, McCracken JM, et al. Reproductive age-associated fibrosis in the stroma of the mammalian ovary[J]. Reproduction, 2016, 152(3):245-260. doi: 10.1530/REP-16-0129.
doi: 10.1530/REP-16-0129 pmid: 27491879 |
| [1] | 白若妍, 王炎强, 陈京霞. 绝经后女性宫内节育器相关卵巢脓肿术后继发脑脓肿一例[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(6): 485-489. |
| [2] | 李安琪, 朱梦一, 王宇, 高敬书, 吴效科. 丹参酮在多囊卵巢综合征治疗中的潜在价值及其机制[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(6): 494-500. |
| [3] | 雷瑞祥, 万怡, 李钰滋, 关德凤, 张学红. 昼夜节律紊乱与多囊卵巢综合征的关系[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(6): 501-505. |
| [4] | 乔新月, 陶爱琳, 冯晓玲, 陈璐. 多囊卵巢综合征伴焦虑、抑郁障碍的相关性研究[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(6): 506-511. |
| [5] | 田德吉尔, 冯晓玲. 肌肉肌醇与D-手性肌醇在多囊卵巢综合征中的研究及应用[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(6): 512-517. |
| [6] | 杨琴, 王涵婷, 曹媛媛, 周军, 王桂玲. 白藜芦醇对卵巢颗粒细胞功能的调节[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(6): 524-528. |
| [7] | 高征, 李梦元, 李博, 梁婧翘, 张雅冬, 许昕. 中药复方干预肥胖型多囊卵巢综合征糖脂代谢异常的Meta分析[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(5): 368-377. |
| [8] | 朱海英, 齐丹丹, 孙平平, 孙娜, 栾素娴. 辅助生殖技术助孕后卵巢过度刺激综合征合并卵巢扭转一例[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(5): 401-405. |
| [9] | 李轩昂, 王婷婷, 相珊, 赵帅, 连方. 铁死亡在多囊卵巢综合征中的研究进展[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(5): 425-429. |
| [10] | 徐晓燕, 王笑璇. 卵巢妊娠破裂三例诊疗体会[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(4): 309-312. |
| [11] | 李丹萍, 连方, 相珊. 二甲双胍治疗多囊卵巢综合征的机制研究新进展[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(4): 343-347. |
| [12] | 王冬雪, 包莉莉, 刘珊, 杨波. 改良灵活拮抗剂方案对卵巢功能正常女性COH结局的影响[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(3): 185-189. |
| [13] | 刘书杰, 李明泽, 张海燕. 卵巢中-低分化支持-间质细胞瘤一例并文献复习[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(3): 207-211. |
| [14] | 石百超, 常惠, 王宇, 卢凤娟, 王凯悦, 关木馨, 马良, 吴效科. 肠道菌群在多囊卵巢综合征中的作用机制[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(3): 238-242. |
| [15] | 谷旭照, 沈豪飞, 高敏, 刘阿慧, 王娜, 杨雯景, 张学红. 双子宫合并卵巢妊娠一例[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(2): 118-120. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||