
国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 192-200.doi: 10.12280/gjszjk.20240629
收稿日期:2024-12-25
出版日期:2025-05-15
发布日期:2025-06-04
通讯作者:
张志刚,E-mail:
WANG Heng-yang, HU Rong, FAN Wei, ZHANG Li-hong, ZHANG Zhi-gang( )
)
Received:2024-12-25
Published:2025-05-15
Online:2025-06-04
Contact:
ZHANG Zhi-gang, E-mail: 摘要:
目的:评价口服营养剂(包括辅酶Q10、维生素E、肌醇和维生素D)对改善男性不育患者精子浓度、精子活力、精子形态、精子数量和精液体积的功效。方法:检索PubMed、Web of Science、Cochrane Library、中国知网(CNKI)、万方数据(Wanfang Data)、维普网(VIP)和中国生物医学文献服务系统(SinoMed),检索时间自建库至2024年9月1日,将所有使用口服营养剂对男性不育患者效果评估的随机对照试验进行网状Meta分析(network Meta-analysis)。结果:本研究共纳入13项研究,涉及1 094例不育男性。网状Meta分析结果显示,与安慰剂相比,肌醇可改善精子浓度(MD=3.88,95%CI:0.59~7.17)。辅酶Q10(MD=6.45,95%CI:3.23~9.67)和肌醇(MD=5.99,95%CI:1.91~10.08)可提高精子活力。辅酶Q10(MD=1.98,95%CI:1.29~2.68)和维生素D+钙(MD=-0.70,95%CI:-1.29~-0.11)可改善精子形态,辅酶Q10(MD=13.84,95%CI:1.49~26.19)也可改善精子数量。维生素D+钙(MD=0.40,95%CI:0.30~0.46)可改善精液体积。维生素D和维生素E与安慰剂相比在5个目标参数上均无显著差异。结论:对于男性不育患者,辅酶Q10、肌醇、维生素D+钙在改善精液质量方面显示出更好的效果。
王恒阳, 胡荣, 樊薇, 张丽洪, 张志刚. 四种常用口服营养剂对男性不育患者精液质量改善的网状Meta分析[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2025, 44(3): 192-200.
WANG Heng-yang, HU Rong, FAN Wei, ZHANG Li-hong, ZHANG Zhi-gang. The Effectiveness of Four Commonly Used Oral Nutraceuticals in Improving the Sperm Quality in Male Infertility: A Network Meta-Analysis[J]. Journal of International Reproductive Health/Family Planning, 2025, 44(3): 192-200.
| 文献 | 国家 | 样本量(例) | 干预措施 | 相关结局 | 年龄(岁) | 干预时间 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | ||||
| Montanino Oliva等[ | 意大利 | 43 | 43 | 肌醇栓剂 | 安慰剂栓剂 | ②⑤ | 25~39 | 25~39 | 直到妊娠 |
| Maghsoumi-Norouzabad等[ | 伊朗 | 43 | 43 | 维生素D 4 000 IU/d | 安慰剂 4 000 IU/d | ②③④⑤ | 35.13±5.51 | 34.44±5.07 | 12周 |
| Sabetian等[ | 伊朗 | 63 | 61 | 维生素E 400 IU/d | 安慰剂 400 IU/d | ②③⑤ | 35.76±7.24 | 36.72±6.61 | 8周 |
| Capece等[ | 意大利 | 28 | 28 | 肌醇1 000 mg, 1次/d | 安慰剂1 000 mg,1次/d | ①②③ | 28.4±6.6 | 28.8±5.2 | 12周 |
| Calogero等[ | 意大利 | 98 | 96 | 肌醇2 000 mg, 2次/d | 安慰剂2 000 mg,1次/d | ①② | 28 | 28 | 12周 |
| Eslamian等[ | 加拿大 | 15 | 16 | 维生素E 600 IU/d | 安慰剂600 IU/d | ①②③④⑤ | 32.80±4.13 | 33.04±4.08 | 12周 |
| Ener等[ | 土耳其 | 22 | 23 | 维生素E 300 mg,2次/d | 安慰剂 300 mg,2次/d | ④ | 26.5±5.0 | 25.2±4.3 | 12周 |
| Safarinejad等[ | 伊朗 | 101 | 102 | CoQ10 200 mg/d | 安慰剂 200 mg/d | ②③④⑤ | 31 | 32 | 26周 |
| Safarinejad[ | 伊朗 | 98 | 96 | CoQ10 300 mg/d | 安慰剂 300 mg/d | ②③④⑤ | 28±9 | 28±10 | 26周 |
| Nadjarzadeh等[ | 伊朗 | 23 | 24 | CoQ10 200 mg/d | 安慰剂 200 mg/d | ①②③ | 34.17±4.52 | 34.67±6.69 | 12周 |
| Balercia等[ | 意大利 | 28 | 27 | CoQ10 200 mg/d | 安慰剂 200 mg/d | ①② | 32 | 32 | 24周 |
| Blomberg Jensen等[ | 丹麦 | 133 | 136 | 维生素D 1 400 IU+钙500 mg/d | 安慰剂 500 mg/d | ①②③④⑤ | 34.3±6.2 | 35.2±6.8 | 24周 |
| Amini等[ | 伊朗 | 31 | 31 | 维生素 D 50 000 IU/周 | 安慰剂 50 000 IU/周 | ①③⑤ | 34.37±4.83 | 34.86±4.65 | 12周 |
表1 纳入文献特征
| 文献 | 国家 | 样本量(例) | 干预措施 | 相关结局 | 年龄(岁) | 干预时间 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | ||||
| Montanino Oliva等[ | 意大利 | 43 | 43 | 肌醇栓剂 | 安慰剂栓剂 | ②⑤ | 25~39 | 25~39 | 直到妊娠 |
| Maghsoumi-Norouzabad等[ | 伊朗 | 43 | 43 | 维生素D 4 000 IU/d | 安慰剂 4 000 IU/d | ②③④⑤ | 35.13±5.51 | 34.44±5.07 | 12周 |
| Sabetian等[ | 伊朗 | 63 | 61 | 维生素E 400 IU/d | 安慰剂 400 IU/d | ②③⑤ | 35.76±7.24 | 36.72±6.61 | 8周 |
| Capece等[ | 意大利 | 28 | 28 | 肌醇1 000 mg, 1次/d | 安慰剂1 000 mg,1次/d | ①②③ | 28.4±6.6 | 28.8±5.2 | 12周 |
| Calogero等[ | 意大利 | 98 | 96 | 肌醇2 000 mg, 2次/d | 安慰剂2 000 mg,1次/d | ①② | 28 | 28 | 12周 |
| Eslamian等[ | 加拿大 | 15 | 16 | 维生素E 600 IU/d | 安慰剂600 IU/d | ①②③④⑤ | 32.80±4.13 | 33.04±4.08 | 12周 |
| Ener等[ | 土耳其 | 22 | 23 | 维生素E 300 mg,2次/d | 安慰剂 300 mg,2次/d | ④ | 26.5±5.0 | 25.2±4.3 | 12周 |
| Safarinejad等[ | 伊朗 | 101 | 102 | CoQ10 200 mg/d | 安慰剂 200 mg/d | ②③④⑤ | 31 | 32 | 26周 |
| Safarinejad[ | 伊朗 | 98 | 96 | CoQ10 300 mg/d | 安慰剂 300 mg/d | ②③④⑤ | 28±9 | 28±10 | 26周 |
| Nadjarzadeh等[ | 伊朗 | 23 | 24 | CoQ10 200 mg/d | 安慰剂 200 mg/d | ①②③ | 34.17±4.52 | 34.67±6.69 | 12周 |
| Balercia等[ | 意大利 | 28 | 27 | CoQ10 200 mg/d | 安慰剂 200 mg/d | ①② | 32 | 32 | 24周 |
| Blomberg Jensen等[ | 丹麦 | 133 | 136 | 维生素D 1 400 IU+钙500 mg/d | 安慰剂 500 mg/d | ①②③④⑤ | 34.3±6.2 | 35.2±6.8 | 24周 |
| Amini等[ | 伊朗 | 31 | 31 | 维生素 D 50 000 IU/周 | 安慰剂 50 000 IU/周 | ①③⑤ | 34.37±4.83 | 34.86±4.65 | 12周 |
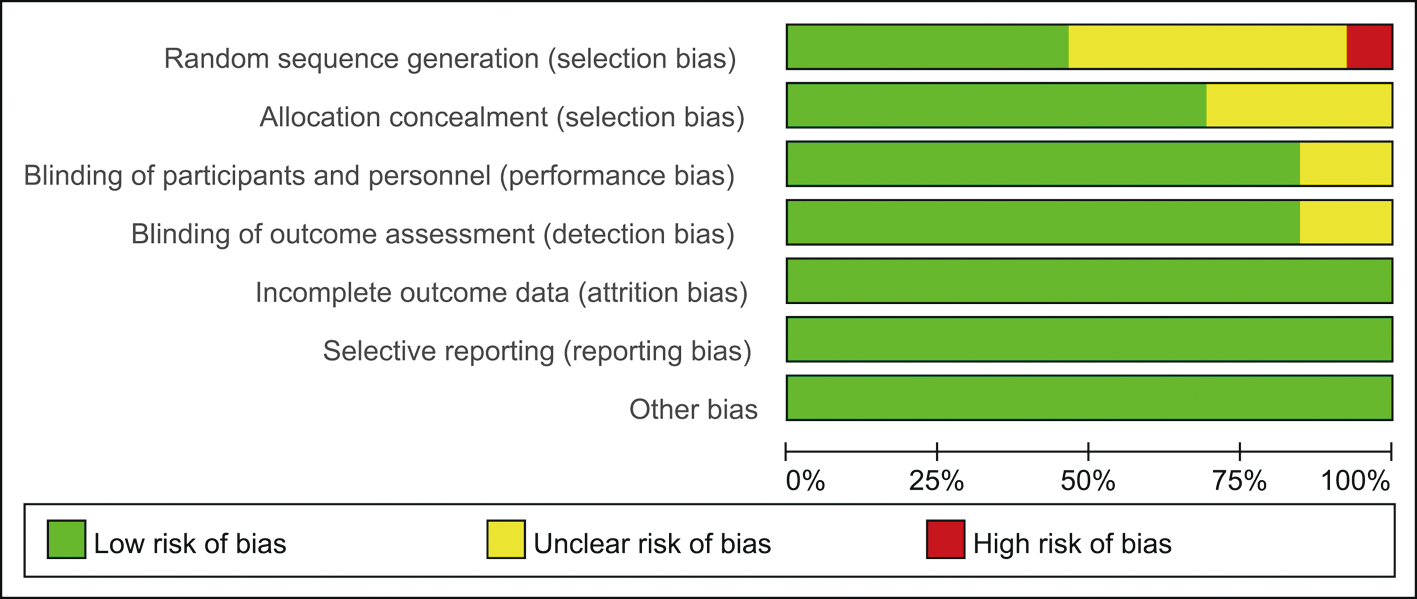
图2 偏倚风险评价结果 注:Random sequence generation 随机序列生成,Allocation concealment 分配隐藏,Blinding of participants and personnel 医生和患者实施盲法,Blinding of outcome assessment 结局评估中的盲法,Incomplete outcome data 结果数据的完整性,Selective reporting 选择性研究结果,Other bias 其他偏倚来源,Low risk of bias 低偏倚风险,Unclear risk of bias 偏倚风险不明确,High risk of bias 高偏倚风险。
| 相关结局 | 干预方法 | 纳入研究(篇) | 异质性检验 | 效应模型 | MD(95%CI) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2 | P | ||||||
| 精子浓度 | 肌醇 | 2[ | 89% | 0.003 | 随机 | 3.86(0.25~7.47) | 0.04 |
| CoQ10 | 2[ | 0% | 0.87 | 固定 | -0.04(-0.43~0.34) | 0.83 | |
| 精子活力 | 肌醇 | 3[ | 72% | 0.03 | 随机 | 5.07(2.01~8.13) | 0.001 |
| 维生素E | 2[ | 0% | 0.85 | 固定 | 0.35(-1.96~2.66) | 0.77 | |
| CoQ10 | 4[ | 98% | <0.000 1 | 随机 | 6.21(1.75~10.68) | 0.006 | |
| 精子形态 | 维生素E | 2[ | 0% | 0.85 | 固定 | -0.13(-0.59~0.34) | 0.59 |
| 维生素D | 2[ | 0% | 0.53 | 固定 | 0.04(-0.43~0.52) | 0.86 | |
| CoQ10 | 3[ | 47% | 0.15 | 固定 | 1.95(1.41~2.50) | <0.000 1 | |
| 精子数量 | 维生素E | 2[ | 84% | 0.01 | 随机 | 7.73(-11.22~26.68) | 0.42 |
| CoQ10 | 2[ | 89% | 0.003 | 随机 | 13.82(5.89~21.76) | 0.000 6 | |
| 精液体积 | 维生素E | 2[ | 0% | 0.71 | 固定 | -0.05(-0.24~0.15) | 0.64 |
| 维生素D | 2[ | 0% | 0.93 | 固定 | -0.23(-0.84~0.37) | 0.45 | |
| CoQ10 | 2[ | 0% | 0.75 | 固定 | -0.05(-0.35~0.25) | 0.73 | |
表2 传统Meta分析结果
| 相关结局 | 干预方法 | 纳入研究(篇) | 异质性检验 | 效应模型 | MD(95%CI) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2 | P | ||||||
| 精子浓度 | 肌醇 | 2[ | 89% | 0.003 | 随机 | 3.86(0.25~7.47) | 0.04 |
| CoQ10 | 2[ | 0% | 0.87 | 固定 | -0.04(-0.43~0.34) | 0.83 | |
| 精子活力 | 肌醇 | 3[ | 72% | 0.03 | 随机 | 5.07(2.01~8.13) | 0.001 |
| 维生素E | 2[ | 0% | 0.85 | 固定 | 0.35(-1.96~2.66) | 0.77 | |
| CoQ10 | 4[ | 98% | <0.000 1 | 随机 | 6.21(1.75~10.68) | 0.006 | |
| 精子形态 | 维生素E | 2[ | 0% | 0.85 | 固定 | -0.13(-0.59~0.34) | 0.59 |
| 维生素D | 2[ | 0% | 0.53 | 固定 | 0.04(-0.43~0.52) | 0.86 | |
| CoQ10 | 3[ | 47% | 0.15 | 固定 | 1.95(1.41~2.50) | <0.000 1 | |
| 精子数量 | 维生素E | 2[ | 84% | 0.01 | 随机 | 7.73(-11.22~26.68) | 0.42 |
| CoQ10 | 2[ | 89% | 0.003 | 随机 | 13.82(5.89~21.76) | 0.000 6 | |
| 精液体积 | 维生素E | 2[ | 0% | 0.71 | 固定 | -0.05(-0.24~0.15) | 0.64 |
| 维生素D | 2[ | 0% | 0.93 | 固定 | -0.23(-0.84~0.37) | 0.45 | |
| CoQ10 | 2[ | 0% | 0.75 | 固定 | -0.05(-0.35~0.25) | 0.73 | |
| 干预措施 | 精子浓度 | 精子活力 | 精子形态 | 精子数量 | 精液体积 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUCRA(%) | 等级 | SUCRA(%) | 等级 | SUCRA(%) | 等级 | SUCRA(%) | 等级 | SUCRA(%) | 等级 | |
| 安慰剂 | 46.7 | 3.7 | 28.5 | 4.6 | 57.7 | 2.7 | 32.7 | 3.7 | 46.9 | 3.1 |
| 维生素E | 46.9 | 3.7 | 31.0 | 4.5 | 45.2 | 3.2 | 63.5 | 2.5 | 32.5 | 3.7 |
| CoQ10 | 42.4 | 3.9 | 82.3 | 1.9 | 100.0 | 1.0 | 88.7 | 1.5 | 32.9 | 3.7 |
| 维生素D | 29.5 | 4.5 | 75.0 | 2.2 | 37.5 | 3.5 | 39.9 | 7.8 | 38.2 | 3.5 |
| 肌醇 | 91.1 | 1.4 | 78.6 | 2.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 维生素D+钙 | 43.4 | 3.8 | 4.6 | 5.8 | 9.6 | 4.6 | 25.3 | 6.5 | 99.4 | 1.0 |
表3 6种干预措施疗效结果的SUCRA值和等级
| 干预措施 | 精子浓度 | 精子活力 | 精子形态 | 精子数量 | 精液体积 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUCRA(%) | 等级 | SUCRA(%) | 等级 | SUCRA(%) | 等级 | SUCRA(%) | 等级 | SUCRA(%) | 等级 | |
| 安慰剂 | 46.7 | 3.7 | 28.5 | 4.6 | 57.7 | 2.7 | 32.7 | 3.7 | 46.9 | 3.1 |
| 维生素E | 46.9 | 3.7 | 31.0 | 4.5 | 45.2 | 3.2 | 63.5 | 2.5 | 32.5 | 3.7 |
| CoQ10 | 42.4 | 3.9 | 82.3 | 1.9 | 100.0 | 1.0 | 88.7 | 1.5 | 32.9 | 3.7 |
| 维生素D | 29.5 | 4.5 | 75.0 | 2.2 | 37.5 | 3.5 | 39.9 | 7.8 | 38.2 | 3.5 |
| 肌醇 | 91.1 | 1.4 | 78.6 | 2.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 维生素D+钙 | 43.4 | 3.8 | 4.6 | 5.8 | 9.6 | 4.6 | 25.3 | 6.5 | 99.4 | 1.0 |
| 干预措施 | 安慰剂 | 维生素E | CoQ10 | 维生素D | 肌醇 | 维生素D+钙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安慰剂 | 0 | |||||
| 维生素E | -0.60(-4.73~4.61) | 0 | ||||
| CoQ10 | -0.06(-7.73~6.17) | -0.54(-8.76~7.68) | 0 | |||
| 维生素D | -2.12(-10.11~5.87) | -2.06(-11.31~7.19) | -1.52(-11.99~8.95) | 0 | ||
| 肌醇 | 3.88(0.59~7.17)* | 3.94(-1.77~9.65) | 4.48(-3.04~12.01) | 6.00(-2.64~14.64) | 0 | |
| 维生素D+钙 | -0.05(-7.58~6.58) | -0.44(-8.91~8.03) | 0.10(-9.69~9.89) | 1.62(-9.05~12.29) | -4.38(-12.19~3.42) | 0 |
表4 精子浓度的网状Meta分析 [MD(95%CI)]
| 干预措施 | 安慰剂 | 维生素E | CoQ10 | 维生素D | 肌醇 | 维生素D+钙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安慰剂 | 0 | |||||
| 维生素E | -0.60(-4.73~4.61) | 0 | ||||
| CoQ10 | -0.06(-7.73~6.17) | -0.54(-8.76~7.68) | 0 | |||
| 维生素D | -2.12(-10.11~5.87) | -2.06(-11.31~7.19) | -1.52(-11.99~8.95) | 0 | ||
| 肌醇 | 3.88(0.59~7.17)* | 3.94(-1.77~9.65) | 4.48(-3.04~12.01) | 6.00(-2.64~14.64) | 0 | |
| 维生素D+钙 | -0.05(-7.58~6.58) | -0.44(-8.91~8.03) | 0.10(-9.69~9.89) | 1.62(-9.05~12.29) | -4.38(-12.19~3.42) | 0 |
| 干预措施 | 安慰剂 | 维生素E | CoQ10 | 维生素D | 肌醇 | 维生素D+钙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安慰剂 | 0 | |||||
| 维生素E | 0.26(-4.35~4.68) | 0 | ||||
| CoQ10 | 6.45(3.23~9.67)* | 6.20(0.58~11.81)* | 0 | |||
| 维生素D | 5.86(-0.53~12.25) | 5.60(-2.27~13.48) | -0.59(-7.75~6.56) | 0 | ||
| 肌醇 | 5.99(1.91~10.08)* | 5.74(-0.42~11.90) | -0.46(-5.69~4.77) | 0.13(-7.45~7.72) | 0 | |
| 维生素D+钙 | -4.00(-9.57~1.57) | -4.26(-11.48~2.97) | -10.45(-16.88~-4.02)* | -9.86(-18.33~-1.39)* | -9.99(-16.90~-3.09)* | 0 |
表5 精子活力的网状Meta分析 [MD(95%CI)]
| 干预措施 | 安慰剂 | 维生素E | CoQ10 | 维生素D | 肌醇 | 维生素D+钙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安慰剂 | 0 | |||||
| 维生素E | 0.26(-4.35~4.68) | 0 | ||||
| CoQ10 | 6.45(3.23~9.67)* | 6.20(0.58~11.81)* | 0 | |||
| 维生素D | 5.86(-0.53~12.25) | 5.60(-2.27~13.48) | -0.59(-7.75~6.56) | 0 | ||
| 肌醇 | 5.99(1.91~10.08)* | 5.74(-0.42~11.90) | -0.46(-5.69~4.77) | 0.13(-7.45~7.72) | 0 | |
| 维生素D+钙 | -4.00(-9.57~1.57) | -4.26(-11.48~2.97) | -10.45(-16.88~-4.02)* | -9.86(-18.33~-1.39)* | -9.99(-16.90~-3.09)* | 0 |
| 干预措施 | 安慰剂 | 维生素E | CoQ10 | 维生素D | 维生素D+钙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安慰剂 | 0 | ||||
| 维生素E | -0.14(-0.84~0.57) | 0 | |||
| CoQ10 | 1.98(1.29~2.68)* | 2.12(1.12~3.12)* | 0 | ||
| 维生素D | -0.26(-1.40~0.88) | -0.12(-1.46~1.22) | -2.24(-3.58~-0.91)* | 0 | |
| 维生素D+钙 | -0.70(-1.29~-0.11)* | -0.56(-1.48~0.35) | -2.68(-3.59~-1.77)* | -0.44(-1.72~0.84) | 0 |
表6 精子形态的网状Meta分析 [MD(95%CI)]
| 干预措施 | 安慰剂 | 维生素E | CoQ10 | 维生素D | 维生素D+钙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安慰剂 | 0 | ||||
| 维生素E | -0.14(-0.84~0.57) | 0 | |||
| CoQ10 | 1.98(1.29~2.68)* | 2.12(1.12~3.12)* | 0 | ||
| 维生素D | -0.26(-1.40~0.88) | -0.12(-1.46~1.22) | -2.24(-3.58~-0.91)* | 0 | |
| 维生素D+钙 | -0.70(-1.29~-0.11)* | -0.56(-1.48~0.35) | -2.68(-3.59~-1.77)* | -0.44(-1.72~0.84) | 0 |
| 干预措施 | 安慰剂 | 维生素E | CoQ10 | 维生素D | 维生素D+钙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安慰剂 | 0 | ||||
| 维生素E | 6.62(-7.97~21.21) | 0 | |||
| CoQ10 | 13.84(1.49~26.19)* | 7.22(-11.89~26.32) | 0 | ||
| 维生素D | 0.84(-16.82~18.50) | -5.78(-28.69~17.12) | -13.00(-34.55~8.55) | 0 | |
| 维生素D+钙 | -5.00(-29.38~19.38) | -11.62(-40.03~16.79) | -18.84(-46.17~8.49) | -5.84(-35.94~24.26) | 0 |
表7 精子数量的网状Meta分析 [MD(95%CI)]
| 干预措施 | 安慰剂 | 维生素E | CoQ10 | 维生素D | 维生素D+钙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安慰剂 | 0 | ||||
| 维生素E | 6.62(-7.97~21.21) | 0 | |||
| CoQ10 | 13.84(1.49~26.19)* | 7.22(-11.89~26.32) | 0 | ||
| 维生素D | 0.84(-16.82~18.50) | -5.78(-28.69~17.12) | -13.00(-34.55~8.55) | 0 | |
| 维生素D+钙 | -5.00(-29.38~19.38) | -11.62(-40.03~16.79) | -18.84(-46.17~8.49) | -5.84(-35.94~24.26) | 0 |
| 干预措施 | 安慰剂 | 维生素E | CoQ10 | 维生素D | 维生素D+钙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安慰剂 | 0 | ||||
| 维生素E | -0.05(-0.24~0.15) | 0 | |||
| CoQ10 | -0.05(-0.35~0.25) | -0.01(-0.36~0.35) | 0 | ||
| 维生素D | -0.03(-0.43~0.37) | 0.01(-0.43~0.46) | 0.02(-0.48~0.52) | 0 | |
| 维生素D+钙 | 0.40(0.30~0.46)* | 0.45(0.23~0.66)* | 0.45(0.14~0.77)* | 0.43(0.02~0.84)* | 0 |
表8 精液体积的网状Meta分析 [MD(95%CI)]
| 干预措施 | 安慰剂 | 维生素E | CoQ10 | 维生素D | 维生素D+钙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安慰剂 | 0 | ||||
| 维生素E | -0.05(-0.24~0.15) | 0 | |||
| CoQ10 | -0.05(-0.35~0.25) | -0.01(-0.36~0.35) | 0 | ||
| 维生素D | -0.03(-0.43~0.37) | 0.01(-0.43~0.46) | 0.02(-0.48~0.52) | 0 | |
| 维生素D+钙 | 0.40(0.30~0.46)* | 0.45(0.23~0.66)* | 0.45(0.14~0.77)* | 0.43(0.02~0.84)* | 0 |
| [1] | Agarwal A, Mulgund A, Hamada A, et al. A unique view on male infertility around the globe[J]. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 2015, 13:37. doi: 10.1186/s12958-015-0032-1. |
| [2] | Illiano E, Trama F, Zucchi A, et al. Resveratrol-Based Multivitamin Supplement Increases Sperm Concentration and Motility in Idiopathic Male Infertility: A Pilot Clinical Study[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9(12):4017. doi: 10.3390/jcm9124017. |
| [3] |
Colpi GM, Francavilla S, Haidl G, et al. European Academy of Andrology guideline Management of oligo-astheno-teratozoospermia[J]. Andrology, 2018, 6(4):513-524. doi: 10.1111/andr.12502.
pmid: 30134082 |
| [4] | 马婧, 韩瑞钰, 梅雪昂, 等. 胰岛素抵抗指数与男性生殖激素水平及精液参数的相关性分析[J]. 中华男科学杂志, 2018, 24(8):695-699. doi: 10.13263/j.cnki.nja.2018.08.005. |
| [5] | Lotti F, Marchiani S, Corona G, et al. Metabolic Syndrome and Reproduction[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(4):1988. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041988. |
| [6] |
Sangouni AA, Taghdir M, Mirahmadi J, et al. Effects of curcumin and/or coenzyme Q10 supplementation on metabolic control in subjects with metabolic syndrome: a randomized clinical trial[J]. Nutr J, 2022, 21(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12937-022-00816-7.
pmid: 36192751 |
| [7] | Lepore E, Lauretta R, Bianchini M, et al. Inositols Depletion and Resistance: Principal Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(13):6796. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136796. |
| [8] | Yoo JY, Yum KS. Effect of Coenzyme Q10 on Insulin Resistance in Korean Patients with Prediabetes: A Pilot Single-Center, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2018, 2018:1613247. doi: 10.1155/2018/1613247. |
| [9] | Nagpal J, Pande JN, Bhartia A. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of the short-term effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on insulin sensitivity in apparently healthy, middle-aged, centrally obese men[J]. Diabet Med, 2009, 26(1):19-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2008.02636.x. |
| [10] | Su L, Qu H, Cao Y, et al. Effect of Antioxidants on Sperm Quality Parameters in Subfertile Men: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials[J]. Adv Nutr, 2022, 13(2):586-594. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmab127. |
| [11] | 庞霁芸, 侯苇, 农玉翔, 等. 人工智能在精子质量分析与精子优选中的应用[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2024, 55(5):1322-1328. doi: 10.12182/20240960603. |
| [12] | Marotta N, Demeco A, Moggio L, et al. Comparative effectiveness of breathing exercises in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Complement Ther Clin Pract, 2020, 41:101260. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2020.101260. |
| [13] | Montanino Oliva M, Buonomo G, Carra MC, et al. Myo-inositol impact on sperm motility in vagina and evaluation of its effects on foetal development[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(5):2704-2709. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202003_20540. |
| [14] | Maghsoumi-Norouzabad L, Zare Javid A, Mansoori A, et al. Vitamin D3 Supplementation Effects on Spermatogram and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Asthenozoospermia Infertile Men: a Randomized, Triple-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial[J]. Reprod Sci, 2022, 29(3):823-835. doi: 10.1007/s43032-021-00769-y. |
| [15] | Sabetian S, Jahromi BN, Vakili S, et al. The Effect of Oral Vitamin E on Semen Parameters and IVF Outcome: A Double-Blinded Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021,2021:5588275. doi: 10.1155/2021/5588275. |
| [16] |
Capece M, Romeo G, Ruffo A, et al. A phytotherapic approach to reduce sperm DNA fragmentation in patients with male infertility[J]. Urologia, 2017, 84(2):79-82. doi: 10.5301/uro.5000210.
pmid: 28058714 |
| [17] |
Calogero AE, Gullo G, La Vignera S, et al. Myoinositol improves sperm parameters and serum reproductive hormones in patients with idiopathic infertility: a prospective double-blind randomized placebo-controlled study[J]. Andrology, 2015, 3(3):491-495. doi: 10.1111/andr.12025.
pmid: 25854593 |
| [18] |
Eslamian G, Amirjannati N, Noori N, et al. Effects of coadministration of DHA and vitamin E on spermatogram, seminal oxidative stress, and sperm phospholipids in asthenozoospermic men: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2020, 112(3):707-719. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqaa124.
pmid: 32453396 |
| [19] |
Ener K, Aldemir M, Isık E, et al. The impact of vitamin E supplementation on semen parameters and pregnancy rates after varicocelectomy: a randomised controlled study[J]. Andrologia, 2016, 48(7):829-834. doi: 10.1111/and.12521.
pmid: 26780969 |
| [20] |
Safarinejad MR, Safarinejad S, Shafiei N, et al. Effects of the reduced form of coenzyme Q10 (ubiquinol) on semen parameters in men with idiopathic infertility: a double-blind, placebo controlled, randomized study[J]. J Urol, 2012, 188(2):526-531. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.03.131.
pmid: 22704112 |
| [21] |
Safarinejad MR. Efficacy of coenzyme Q10 on semen parameters, sperm function and reproductive hormones in infertile men[J]. J Urol, 2009, 182(1):237-248. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.02.121.
pmid: 19447425 |
| [22] |
Nadjarzadeh A, Shidfar F, Amirjannati N, et al. Effect of Coenzyme Q10 supplementation on antioxidant enzymes activity and oxidative stress of seminal plasma: a double-blind randomised clinical trial[J]. Andrologia, 2014, 46(2):177-183. doi: 10.1111/and.12062.
pmid: 23289958 |
| [23] |
Balercia G, Buldreghini E, Vignini A, et al. Coenzyme Q10 treatment in infertile men with idiopathic asthenozoospermia: a placebo-controlled, double-blind randomized trial[J]. Fertil Steril, 2009, 91(5):1785-1792. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.02.119.
pmid: 18395716 |
| [24] |
Blomberg Jensen M, Lawaetz JG, Petersen JH, et al. Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on Semen Quality, Reproductive Hormones, and Live Birth Rate: A Randomized Clinical Trial[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2018, 103(3):870-881. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-01656.
pmid: 29126319 |
| [25] | Amini L, Mohammadbeigi R, Vafa M, et al. Evaluation of the effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on quantitative and qualitative parameters of spermograms and hormones in infertile men: A Randomized controlled trial[J]. Complement Ther Med, 2020, 53:102529. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2020.102529. |
| [26] | De Luca MN, Colone M, Gambioli R, et al. Oxidative Stress and Male Fertility: Role of Antioxidants and Inositols[J]. Antioxidants(Basel), 2021, 10(8):1283. doi: 10.3390/antiox10081283. |
| [27] | Aitken RJ, Drevet JR. The Importance of Oxidative Stress in Determining the Functionality of Mammalian Spermatozoa: A Two-Edged Sword[J]. Antioxidants(Basel), 2020, 9(2):111. doi: 10.3390/antiox9020111. |
| [28] |
Kothari S, Thompson A, Agarwal A, et al. Free radicals: their beneficial and detrimental effects on sperm function[J]. Indian J Exp Biol, 2010, 48(5):425-435.
pmid: 20795359 |
| [29] | Zańko A, Siewko K, Krętowski AJ, et al. Lifestyle, Insulin Resistance and Semen Quality as Co-Dependent Factors of Male Infertility[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 20(1):732. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010732. |
| [30] |
Morrison CD, Brannigan RE. Metabolic syndrome and infertility in men[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol, 2015, 29(4):507-515. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2014.10.006.
pmid: 25487258 |
| [31] |
Adnan E, Rahman IA, Faridin HP. Relationship between insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome components and serum uric acid[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr, 2019, 13(3):2158-2162. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2019.04.001.
pmid: 31235151 |
| [32] | 张国忠, 胡艳梅, 杨宗富. 肌醇治疗不育男性有效性的Meta分析[J]. 中国性科学, 2021, 30(11):5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1993.2021.11.002. |
| [33] | Condorelli RA, La Vignera S, Mongioì LM, et al. Myo-inositol as a male fertility molecule: speed them up![J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2017, 21(Suppl 2):30-35. |
| [34] |
Condorelli RA, La Vignera S, Bellanca S, et al. Myoinositol: does it improve sperm mitochondrial function and sperm motility?[J]. Urology, 2012, 79(6):1290-1295. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2012.03.005.
pmid: 22656408 |
| [35] | 杨明根, 郑周达, 许振强, 等. 辅酶Q10治疗特发性少弱畸形精子症有效性与安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2016, 16(9):1090-1096. doi: 10.7507/1672-2531.20160166. |
| [36] | Groneberg DA, Kindermann B, Althammer M, et al. Coenzyme Q10 affects expression of genes involved in cell signalling, metabolism and transport in human CaCo-2 cells[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2005, 37(6):1208-1218. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2004.11.017. |
| [37] |
Gvozdjakova A, Kucharska J, Lipkova J, et al. Importance of the assessment of coenzyme Q10, alpha-tocopherol and oxidative stress for the diagnosis and therapy of infertility in men[J]. Bratisl Lek Listy, 2013, 114(11):607-609. doi: 10.4149/bll_2013_129.
pmid: 24236426 |
| [38] |
Salas-Huetos A, Rosique-Esteban N, Becerra-Tomás N, et al. The Effect of Nutrients and Dietary Supplements on Sperm Quality Parameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials[J]. Adv Nutr, 2018, 9(6):833-848. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmy057.
pmid: 30462179 |
| [39] | Li KP, Yang XS, Wu T. The Effect of Antioxidants on Sperm Quality Parameters and Pregnancy Rates for Idiopathic Male Infertility: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2022, 13:810242. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.810242. |
| [40] |
Ramlau-Hansen CH, Moeller UK, Bonde JP, et al. Are serum levels of vitamin D associated with semen quality? Results from a cross-sectional study in young healthy men[J]. Fertil Steril, 2011, 95(3):1000-1004. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2010.11.002.
pmid: 21122842 |
| [41] |
Abbasihormozi S, Kouhkan A, Alizadeh AR, et al. Association of vitamin D status with semen quality and reproductive hormones in Iranian subfertile men[J]. Andrology, 2017, 5(1):113-118. doi: 10.1111/andr.12280.
pmid: 27792863 |
| [42] | Blomberg Jensen M, Gerner Lawaetz J, Andersson AM, et al. Vitamin D deficiency and low ionized calcium are linked with semen quality and sex steroid levels in infertile men[J]. Hum Reprod, 2016, 31(8):1875-1885. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew152. |
| [43] |
Hammoud AO, Meikle AW, Peterson CM, et al. Association of 25-hydroxy-vitamin D levels with semen and hormonal parameters[J]. Asian J Androl, 2012, 14(6):855-859. doi: 10.1038/aja.2012.77.
pmid: 23042450 |
| [44] | Aquila S, Guido C, Middea E, et al. Human male gamete endocrinology: 1alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25(OH)2D3) regulates different aspects of human sperm biology and metabolism[J]. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 2009, 7:140. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-7-140. |
| [45] | Yahyavi SK, Boisen IM, Cui Z, et al. Calcium and vitamin D homoeostasis in male fertility[J]. Proc Nutr Soc, 2024, 83(2):95-108. doi: 10.1017/S002966512300486X. |
| [46] | 刘建家, 曾健文, 何宇, 等. 显微镜精索静脉结扎术联合维生素E改善精子DNA完整性和受孕结局的研究[J]. 生殖医学杂志, 2024, 33(4):521-525. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3845.2024.04.016. |
| [47] | 孙迪, 王楠楠, 张科, 等. 维生素E在男性不育症治疗中的临床应用研究进展[J]. 中国性科学, 2018, 27(7):12-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1993.2018.07.002. |
| [1] | 李苗, 李希西, 程敏, 刘航呈. 中国不孕女性体外受精-胚胎移植治疗期抑郁症状检出率的Meta分析[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2025, 44(3): 184-191. |
| [2] | 马颖琪, 李佳丽, 冯梦枝, 石百超, 王宇, 高敬书, 吴效科. 基于PI3K/Akt信号通路探讨中药单体及复方治疗多囊卵巢综合征的机制[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2025, 44(3): 220-226. |
| [3] | 刘彤瑶, 晁春娥, 田宁, 历晨雪, 马瑞红, 夏天. 社会心理支持在女性生殖障碍性疾病中的应用[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2025, 44(3): 232-235. |
| [4] | 张梦宇, 尹耀学, 侯振. 子宫内膜异位症相关未破裂卵泡黄素化综合征的研究进展[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2025, 44(3): 253-258. |
| [5] | 戴凯妹, 张晶晶, 程世斌, 赵倩, 郝胜菊, 王兴. 2号染色体臂间倒位合并罗伯逊易位一家系的遗传学分析[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2025, 44(2): 125-127. |
| [6] | 谢雷, 田梅梅, 徐于睿, 黄欣, 周艳茂, 徐颖, 卜桦, 奚慧琴. 不孕症初诊夫妻生育压力、二元应对及生育生活质量的调查[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2025, 44(2): 89-94. |
| [7] | 陈小燕, 张娟, 赵纯, 季娟, 赵静. 男性久坐行为与精子质量及辅助生殖结局的相关性研究[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2025, 44(2): 95-99. |
| [8] | 贾声晓, 孙淼, 匡洪影, 徐博雅. 微小RNA参与多囊卵巢综合征胰岛素抵抗的研究进展[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2025, 44(1): 59-64. |
| [9] | 徐姗, 孟江萍. 辅助生殖技术中精子DNA损伤的研究现状[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2025, 44(1): 71-77. |
| [10] | 田德吉尔, 冯晓玲. 肌肉肌醇与D-手性肌醇在多囊卵巢综合征中的研究及应用[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(6): 512-517. |
| [11] | 杨琴, 王涵婷, 曹媛媛, 周军, 王桂玲. 白藜芦醇对卵巢颗粒细胞功能的调节[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(6): 524-528. |
| [12] | 李轩昂, 王婷婷, 相珊, 赵帅, 连方. 铁死亡在多囊卵巢综合征中的研究进展[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(5): 425-429. |
| [13] | 陈小均, 刘豫月, 孔涛, 王成李, 刘昭文, 张志杰. 附睾多发炎性肌纤维母细胞瘤一例[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(4): 313-316. |
| [14] | 焦梦文, 张月文, 王玲, 莫少康. 环状RNA在生殖系统的研究进展[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(4): 322-327. |
| [15] | 张爱玉, 栾翠玉, 王冬梅, 蒋帅. IVF-ET不孕症患者就医延迟现状及影响因素分析[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2024, 43(3): 190-194. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||